Building a better tomorrow using the sustainability radar
In this guest post, Mattie Yeta, chief sustainability officer at IT consultancy CGI, sets out a fresh approach for enterprises that want to keep tabs on their sustainability track record
While many organisations recognise the importance of sustainability, we still have a way to go. The recent IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), acknowledges the interdependence of climate, people and biodiversity, and integrates natural, economic science and social more strongly than earlier IPCC assessments. The report advises that to avoid mounting loss of life and biodiversity, ambitious and accelerated action is required to cut greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change.
In a world where the constantly changing relationships between environmental, social, and financial issues are becoming more and more evident, organisations that remain unaware of their impacts and dependencies will fail to recognise new opportunities for growth, development, efficiency, and resilience. They will also provoke unnecessary risk.
Today, technology is a significant contributor to climate change. Most organisations are attempting to address this by building energy-efficient datacentres, analysing operations and activities, adopting renewable energy sources, analysing supply chains, or developing applications that consume less energy in ongoing operations and their creation.
Making sustainable decisions is something an increasing number of stakeholders aim to do. Businesses are incorporating sustainability considerations directly into technological strategies. CGI has developed a sustainability technology radar to facilitate sustainable decision making.
CGI announced its science-based targets independently verified by the Science-Based Targets initiative . That means business decisions are made based on complete information leading to efficient outcomes for the organisation and society. CGI is now accelerating its strategic approach through the sustainability technology radar, which helps understand the dynamic relationships between technology and sustainable development.
Our understanding of the technology helps to rethink the negative and positive impacts and shifts the perception of making corporate decisions with sustainability in mind. In addition, the framework provides the tools to identify and measure the value received from natural capital, intellectual capital, social capital, financial capital, produced capital and human capital leading to integrated decision-making.
So what is the sustainability technology radar and what does it do?
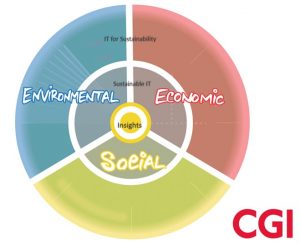
- Insights
Data insights enable organisations to understand information by analysing it to make decisions. Active intelligence, for example, provide real-time data for immediate actions.
Actionable data insights are relevant and specific. They lead to actions which increase efficiency, for example.
- Sustainable Technology
Technologies that transform the internal operations
- IT for sustainability
Technologies that transform activities external to the organisation. For example, carbon capture technologies.
- Sustainability Pillars
These are simply known as environmental (for example, nature), Social (for example, modern slavery) and economic (for example, optimisation).
Understanding the holistic relationships and dependencies through the sustainability radar enables the organisation to consider and reprioritise the protection, resilience, and health of undervalued resources, leading to the cascading of benefits throughout the system.


