Syda Productions - stock.adobe.c
Invest in cyber security with confidence using a structured approach
Cyber security has never been more challenging or important in rapidly changing business, regulatory, IT and threat environments. There is a need for a more structured approach to investment
The cyber security challenge has never been greater because of the continually expanding attack surface as the shift to mobile, cloud and other technologies supporting digital transformation gains momentum. These technologies provide increasing opportunities for attackers. At the same time, attackers are becoming ever better skilled, organised and resourced to produce ever-increasing volumes of malware and other attacks that can adapt to targeted environments and evade detection. Also, attackers are using automation to expedite their operations.
The increasing threats and exposure mean that cyber security is essential to businesses remaining productive and competitive, as well as compliant with a growing raft of national, regional and international cyber security and privacy regulations.
Cyber security is climbing the board agenda and corporate priority list for a growing number of businesses as business leaders increasingly understand that they need to go beyond mere compliance to ensure they have the necessary cyber security capabilities to keep the business running and keep data safe. Data protection is vital to protect intellectual property and instil trust in employees, partners and customers.
Cyber security increasingly a strategic goal
In response to the changing vulnerabilities and threats, and the increased need to build trust for competitive advantage, business leaders are making cyber security a strategic goal. There is now greater understanding that cyber security should not be an afterthought driven by compliance, but must be an integral part of company organisation and processes if the business is to survive and remain competitive.
Comprehensive cyber security, therefore, needs to be the goal of every successful business, and can be achieved by following a modern cyber security framework or architecture. Cyber security tools are essential to enabling organisations to protect data, detect malicious activity, respond to attacks and recover from them quickly to minimise the impact on business operations.
It is also important to remember that cyber security is not only about protecting the business against specific threats, but essentially about providing the cyber protections that the business needs to be viable. Cyber security is therefore about working with the business to ensure that the business can innovate and achieve its goal by ensuring a safe IT environment to operate in.
In the same way that the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre is aiming to make the UK a safe place to do business, each business needs to work with its cyber security teams to ensure the organisation’s IT environment is a safe place to do business for employees, partners and customers.
The cyber security industry is evolving in response to changing market requirements by providing new types of tools and capabilities. And given the increasing importance of cyber security systems and tools to business, the overall cyber security market will continue to evolve and grow in importance, size and value.
Those sub-sections of the market that support digital transformation, including the move to the cloud, will see the greatest evolution, investment and growth, while more traditional security technologies are likely to experience some decline, especially those focused on on-premise use cases and legacy systems.
The role of a cyber security architecture
To understand what technologies and capabilities are relevant to cyber security, where they fit in, and their main role, organisations need to map the systems they already have against a security reference architecture.
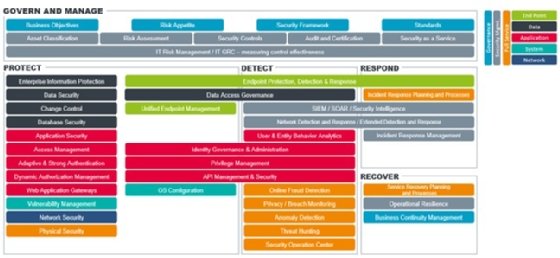
Most modern security reference architectures feature five essential building blocks of a comprehensive and effective modern approach to cyber security:
- Govern and manage
- Protect
- Detect
- Respond
- Recover
Each of these building blocks includes several key components or capabilities that are essential to achieve a good level of cyber security.
In other words, cyber security capabilities (technologies and processes) fall into the overarching govern and manage block or one or more of the four pillars of cyber security: protect, detect, respond and recover.
Govern and manage
The govern and manage block includes everything required for an overarching approach to maintaining a security architecture and maintaining security. The components in the govern and manage block are relevant for all areas of cyber security and form the base of the reference architecture.
Within the govern and manage block, we find governance elements such as business objectives, risk appetite, security framework and standards, and security management elements such as asset classification, risk assessment, security controls, audit and certification, security as a service, IT risk management, and IT governance, risk and control. This block is about using a risk-based approach to identify risks that must be mitigated by using the four other pillars.
A security reference architecture also typically references five main technology “layers”:
- Endpoint
- Data
- Application
- System
- Network
Additional overarching layers are:
- Governance
- Security management
- Full service
Full service highlights those components that cover all five of the main cyber security layers.
Protect, detect, respond, recover
The protect pillar includes everything that has to do with protecting data, including change controls, access controls, vulnerability management, and network and physical security. It also includes several components that span one or two other pillars, such as endpoint protection, detection and response (which also spans the detect and respond pillars).
The detect pillar includes everything related to detecting threats and anomalous or malicious activity. Several components span one or two other pillars, such as the SIEM/security intelligence component. The detect pillar also includes five “full-service” components that cover all layers of cyber security, namely: online fraud detection, privacy/breach monitoring, anomaly detection, threat hunting and security operations centre.
The respond pillar is becoming increasingly important as organisations realise they cannot rely only on protection technologies to keep cyber attackers out of their corporate networks and must have some capacity to respond when security breaches do occur. The respond pillar includes components that are designed to ensure that when an organisation’s cyber defences are breached, the impact of the attack is kept to an absolute minimum. The focus of this block is on incident response.
The recover pillar includes components that are designed to ensure that in the event of a cyber attack, basic business processes either continue to run or are returned to operation as quickly as possible. This typically includes things like malware removal, roll-back of nodes to the last known good state, placing more zero-trust rules in areas where the attack took place, auditing user accounts, resetting or removing credentials, and identifying security gaps or vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
Operational resilience is a key component and another increasingly important area of focus in the cyber defence arsenal. Ensuring that a business can continue to operate and recover quickly from cyber attacks is essential to reducing the impact of attacks and ensuring the long-term survival of the organisation.
Recommendations
Organisations should ascertain what security technologies and capabilities they have and compare that with a modern cyber security reference architecture, such as the one described above, to identify the gaps.
The next step is to decide in which order the gaps need to be filled based on a risk analysis, followed by drawing up an implementation plan. In this way, organisations can adopt a structured approach to cyber security investments that ensures that the greatest risks are addressed as a priority.











